Pressure Control Using a Pinch Valve: Non-Linear Control Output
- Overview
- Running the Scripts
- Code Example 1: Pressure Model Simulation
- Code Example 2: Complex PID Controller for the Pinch Valve
Overview
This guide aims to demonstrate how to implement a pressure control system using a Pinch Valve. The complexity lies in the unique characteristics of a Pinch Valve, which squeezes an elastomeric tube to regulate back pressure. The valve's flow coefficient (Cv) varies in a non-linear fashion with the valve's plunger position (percentage of travel, from full close to full open). This adds an extra layer of complexity to the control system.
As the valve pinches the tube, the effective opening size and shape change non-linearly. Consequently, the Cv (valve flow coefficient) also changes non-linearly with the percentage of valve opening.
Addressing Non-Linearity through Complex PID Scheduling
To manage this non-linearity, the controller must be designed to operate differently in various regions of operation. Specifically, when the total percentage of the valve's opening is small, the maximum control output change (delta_limit) has to be very small to avoid overshooting or other adverse effects.
The PID controller code includes a scheduling system that changes the control parameters based on the operating conditions. Here's a snippet of that part:
# Define multiple schedules with different controller settings
for error_range, control_range, delta_limit, dead_zone in [
((-50, 50), None, 0.00005, 10),
((-250, 250), None, 0.0005, None),
((-10000, 0), None, 0.05, None),
(None, (0, 0.3), 0.020, None),
(None, None, 0.050, None),
]:
params = ScheduleParameters()
params.kp = -1.0
params.dead_zone = dead_zone
params.delta_limit = delta_limit
constraints = ScheduleConstraints()
constraints.error = error_range
constraints.control = control_range
sched = Schedule(params, constraints)
p.add_schedule(sched)
This scheduling system allows the controller to operate with different settings, including a dead zone, delta limits, and control ranges, depending on the state of the system. This makes it adaptable and more accurate, particularly when dealing with the non-linear characteristics of the Pinch Valve.
Running the Scripts
To run the simulation and control, you'll need to execute two separate Python scripts in sequence:
-
Pressure Model Simulation (
model.py): First, run themodel.pyscript to simulate the pressure control system. Execute this command in your terminal:python3 examples/pid/pinch_valve/model.py -r 0 -
Complex PID Controller (
pid.py): Oncemodel.pyis running, execute thepid.pyscript. This will set up a PID controller to regulate the Pinch Valve based on the pressure readings. Run this command:python3 -i examples/pid/pinch_valve/pid.py
Note: It's crucial to run model.py before executing pid.py to ensure the simulation environment is initialized correctly.
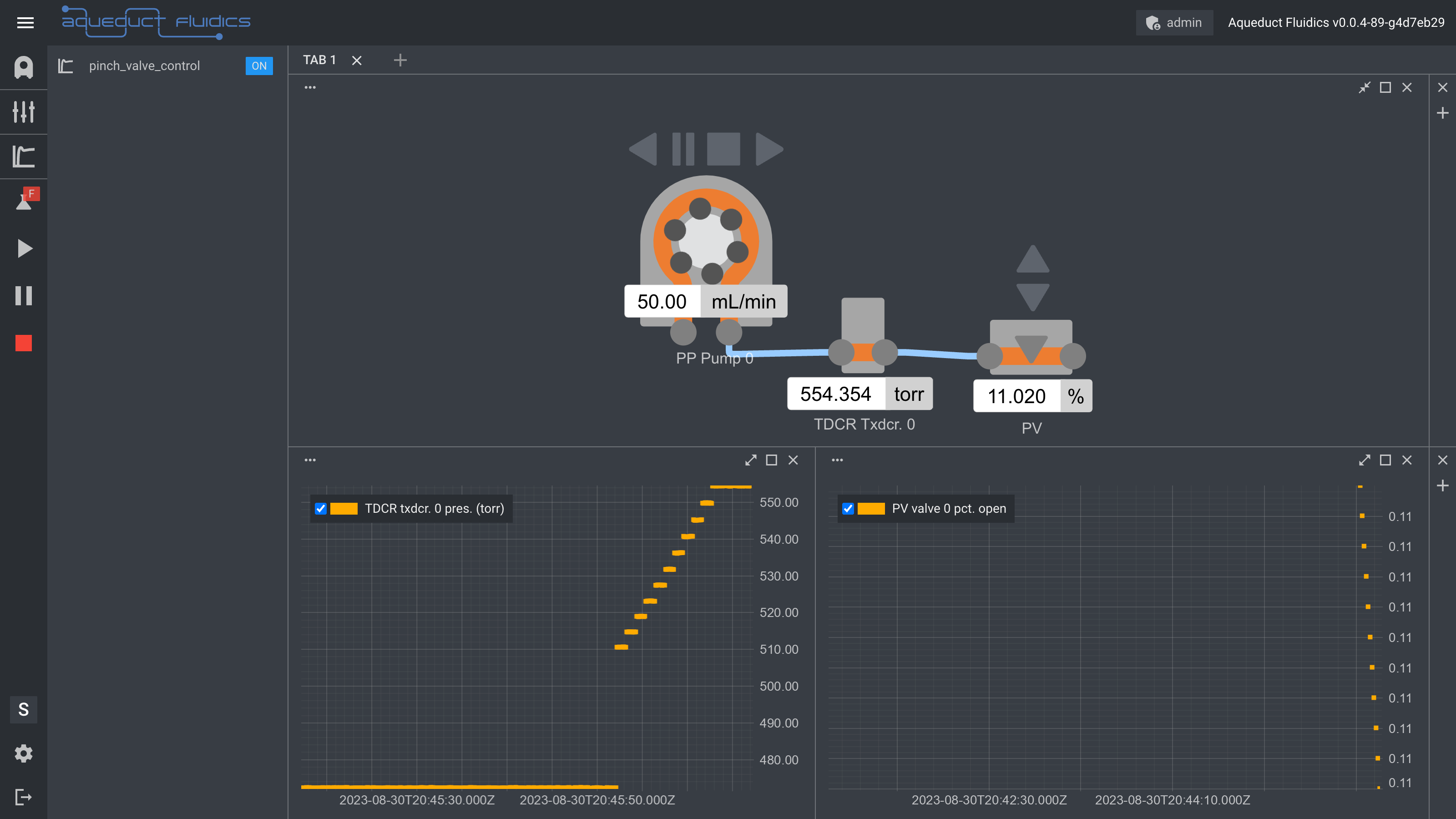
Code Example 1: Pressure Model Simulation
Imports
import argparse
import time
from aqueduct.core.aq import Aqueduct
from aqueduct.core.aq import InitParams
from aqueduct.devices.base.utils import DeviceTypes
from aqueduct.devices.pressure.transducer import PressureTransducer
from aqueduct.devices.pressure.transducer import PressureUnits
from aqueduct.devices.pump.peristaltic import PeristalticPump
from aqueduct.devices.valve.pinch import PinchValve
The PressureModel Class
The PressureModel class simulates a pressure control system using various devices such as a pump, pinch valve, and pressure transducer.
class PressureModel:
def __init__(self, pump: PeristalticPump, pinch_valve: PinchValve, transducer: PressureTransducer, aqueduct: "Aqueduct"):
self.pump = pump
self.pv = pinch_valve
self.tdcr = transducer
self.aq = aqueduct
# ...
Here's the full code for the model:
"""
Demo code demonstrating pressure estimation using a simple model for Aqueduct devices.
"""
# Import necessary modules
import argparse
import time
from aqueduct.core.aq import Aqueduct
from aqueduct.core.aq import InitParams
from aqueduct.devices.base.utils import DeviceTypes
from aqueduct.devices.pressure.transducer import PressureTransducer
from aqueduct.devices.pressure.transducer import PressureUnits
from aqueduct.devices.pump.peristaltic import PeristalticPump
from aqueduct.devices.valve.pinch import PinchValve
class PressureModel:
"""
Simple model for estimating pressures in a filtration process using Aqueduct devices.
"""
filtration_start_time: float = None
filter_cv_retentate: float = 60
def __init__(
self,
pump: PeristalticPump,
pinch_valve: PinchValve,
transducer: PressureTransducer,
aqueduct: "Aqueduct",
):
self.pump = pump
self.pv = pinch_valve
self.tdcr = transducer
self.aq = aqueduct
@staticmethod
def calc_pv_cv(PV) -> float:
"""
Calculate the Cv of the pinch valve.
:param PV: Pinch valve position.
:type PV: float
:return: Cv of the pinch valve.
:rtype: float
"""
if PV < 0.35:
return max(100 - (1 / PV**2), 1)
else:
return 100
def calc_p1(self, R1, PV) -> float:
"""
Calculate the pressure drop between retentate and permeate.
:param R1: Flow rate in the pass-through leg of the TFF filter.
:type R1: float
:param PV: Pinch valve position.
:type PV: float
:return: Pressure drop between retentate and permeate.
:rtype: float
"""
try:
return 1 / (PressureModel.calc_pv_cv(PV) * 0.865 / R1) ** 2
except ZeroDivisionError:
return 0
def calc_pressures(self):
"""
Calculate and update the pressures using the model equations.
"""
p1 = self.calc_p1(self.pump.live[0].ml_min, self.pv.live[0].pct_open)
p1 = min(p1, 50)
self.tdcr.set_sim_values(values=(p1,), units=PressureUnits.PSI)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Parse the initialization parameters from the command line
params = InitParams.parse()
# Initialize the Aqueduct instance with the provided parameters
aq = Aqueduct(
params.user_id,
params.ip_address,
params.port,
register_process=params.register_process,
)
# Perform system initialization if specified
aq.initialize(params.init)
# Set a delay between sending commands to the pump
aq.set_command_delay(0.05)
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument(
"-c",
"--clear",
type=int,
help="clear and create the setup (either 0 or 1)",
default=1,
)
args, _ = parser.parse_known_args()
clear = bool(args.clear)
# Define names for devices
PUMP_NAME = "PP"
XDCR_NAME = "TDCR"
PV_NAME = "PV"
if clear:
# Clear the existing setup and add devices
aq.clear_setup()
aq.add_device(DeviceTypes.PERISTALTIC_PUMP, PUMP_NAME, 1)
aq.add_device(DeviceTypes.PRESSURE_TRANSDUCER, XDCR_NAME, 1)
aq.add_device(DeviceTypes.PINCH_VALVE, PV_NAME, 1)
# Retrieve the setup to confirm the added devices
aq.get_setup()
# Retrieve device instances
pp: PeristalticPump = aq.devices.get(PUMP_NAME)
tdcr: PressureTransducer = aq.devices.get(XDCR_NAME)
pv: PinchValve = aq.devices.get(PV_NAME)
# Create an instance of the PressureModel
model = PressureModel(pp, pv, tdcr, aq)
# Continuous pressure calculation loop
while True:
model.calc_pressures()
time.sleep(0.1)
Code Example 2: Complex PID Controller for the Pinch Valve
Imports
from aqueduct.core.aq import Aqueduct
from aqueduct.core.aq import InitParams
from aqueduct.core.pid import Pid
from aqueduct.core.pid import Schedule
from aqueduct.core.pid import ScheduleConstraints
from aqueduct.core.pid import ScheduleParameters
from aqueduct.devices.pressure.transducer import PressureTransducer
from aqueduct.devices.pump.peristaltic import PeristalticPump
from aqueduct.devices.valve.pinch import PinchValve
Device Retrieval
pp: PeristalticPump = aq.devices.get(PUMP_NAME)
tdcr: PressureTransducer = aq.devices.get(XDCR_NAME)
pv: PinchValve = aq.devices.get(PV_NAME)
PID Controller Setup
The PID controller is set up with multiple schedules to adapt to the system's non-linear nature.
# Define PID controller parameters
process = tdcr.to_pid_process_value(index=0)
control = pv.to_pid_control_output(index=0)
p = Pid(500)
Here's the full code for PID control:
"""
Demonstration of setting up a PID controller with Aqueduct devices.
"""
# Import necessary modules
from aqueduct.core.aq import Aqueduct
from aqueduct.core.aq import InitParams
from aqueduct.core.pid import Pid
from aqueduct.core.pid import Schedule
from aqueduct.core.pid import ScheduleConstraints
from aqueduct.core.pid import ScheduleParameters
from aqueduct.devices.pressure.transducer import PressureTransducer
from aqueduct.devices.pump.peristaltic import PeristalticPump
from aqueduct.devices.valve.pinch import PinchValve
# Parse the initialization parameters from the command line
params = InitParams.parse()
# Initialize the Aqueduct instance with the provided parameters
aq = Aqueduct(params.user_id, params.ip_address, params.port)
# Perform system initialization if specified
aq.initialize(params.init)
# Set a delay between sending commands to the pump
aq.set_command_delay(0.05)
# Define names for devices
PUMP_NAME = "PP"
XDCR_NAME = "TDCR"
PV_NAME = "PV"
# Retrieve the setup to confirm the added devices
aq.get_setup()
# Retrieve device instances
pp: PeristalticPump = aq.devices.get(PUMP_NAME)
tdcr: PressureTransducer = aq.devices.get(XDCR_NAME)
pv: PinchValve = aq.devices.get(PV_NAME)
# Define PID controller parameters
process = tdcr.to_pid_process_value(index=0)
control = pv.to_pid_control_output(index=0)
p = Pid(500)
# Define multiple schedules with different controller settings
for error_range, control_range, delta_limit, dead_zone in [
((-50, 50), None, 0.00005, 10),
((-250, 250), None, 0.0005, None),
((-10000, 0), None, 0.05, None),
(None, (0, 0.3), 0.020, None),
(None, None, 0.050, None),
]:
params = ScheduleParameters()
params.kp = -1.0
params.dead_zone = dead_zone
params.delta_limit = delta_limit
constraints = ScheduleConstraints()
constraints.error = error_range
constraints.control = control_range
sched = Schedule(params, constraints)
p.add_schedule(sched)
# Set output limits for the PID controller
p.output_limits = (0.1, 1)
# Create a PID controller instance using Aqueduct
pid = aq.pid_controller("pinch_valve_control", process, control, p)