PID Control for Peristaltic Pump and Balance
- Introduction
- Imports
- Device Configuration
- PID Controller
- PID Control Loop
- Modification of PID Parameters
Introduction
This guide walks you through a sample code that demonstrates how to implement PID control to control the rate of a peristaltic pump based on the weight reading from a balance. The code performs tasks like setting up the devices, configuring PID parameters, and running control loops.
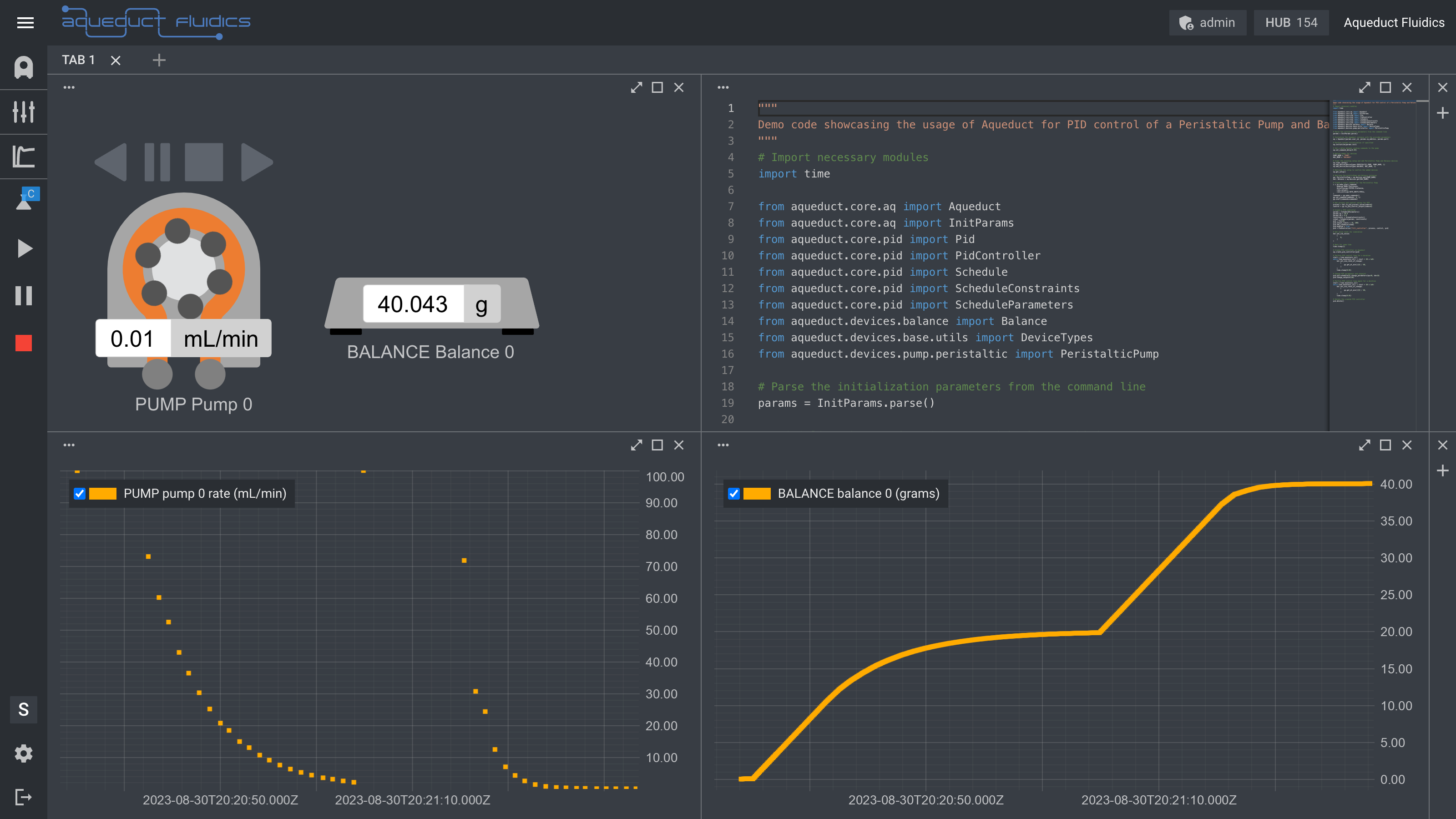
Imports
The first step is to import all the necessary modules from the Aqueduct library.
# Import necessary modules
import time
from aqueduct.core.aq import Aqueduct
from aqueduct.core.aq import InitParams
from aqueduct.core.pid import Pid
from aqueduct.core.pid import PidController
from aqueduct.core.pid import Schedule
from aqueduct.core.pid import ScheduleConstraints
from aqueduct.core.pid import ScheduleParameters
from aqueduct.devices.balance import Balance
from aqueduct.devices.base.utils import DeviceTypes
from aqueduct.devices.pump.peristaltic import PeristalticPump
Initialization
Here, initialization parameters are parsed from the command line and used to initialize the Aqueduct instance.
# Parse the initialization parameters from the command line
params = InitParams.parse()
# Initialize the Aqueduct instance with the provided parameters
aq = Aqueduct(params.user_id, params.ip_address, params.port)
Device Configuration
Clear Setup
Any existing setup should be cleared before adding new devices.
# Clear the existing setup
aq.clear_setup()
Add Devices
This section adds a peristaltic pump and a balance to the setup and then retrieves the newly added devices.
# Add Peristaltic Pump and Balance devices
aq.add_device(DeviceTypes.PERISTALTIC_PUMP, PUMP_NAME, 1)
aq.add_device(DeviceTypes.BALANCE, BAL_NAME, 1)
# Retrieve the setup to confirm the added devices
aq.get_setup()
# Retrieve PeristalticPump and Balance instances
pp: PeristalticPump = aq.devices.get(PUMP_NAME)
bal: Balance = aq.devices.get(BAL_NAME)
PID Controller
PID Parameters and Schedule
Define the PID schedule parameters and constraints. Each PID controller can have multiple schedules. Constraints help to determine which schedule is used at each time step.
# Create a PID controller
params = ScheduleParameters()
params.kp = 10.0
params.kd = 5.0
constraints = ScheduleConstraints()
sched = Schedule(params, constraints)
Creating the PID Controller
The PID controller is then created with the defined schedules.
# Get process and control values for PID
process = bal.to_pid_process_value(index=0)
control = pp.to_pid_control_output(index=0)
pid = PidController("fill_controller", process, control, pid)
PID Control Loop
The code then runs a PID control loop to control the device for a duration.
# Perform PID control loop for a duration
start = time.monotonic_ns()
while time.monotonic_ns() < start + 30 * 1e9:
# set the sim rate of change of the balance based on the pump rate
bal.set_sim_rates_of_change(
[
pp.get_ml_min()[0] / 60,
]
)
time.sleep(0.01)
Modification of PID Parameters
Finally, the code shows how to modify PID parameters and rerun the control loop.
# Change PID parameters and setpoint
pid.pid.schedule[0].change_parameters(kp=30, kd=10)
pid.change_setpoint(40)
Here's the full code:
"""
Demo code showcasing the usage of Aqueduct for PID control of a Peristaltic Pump and Balance.
"""
# Import necessary modules
import time
from aqueduct.core.aq import Aqueduct
from aqueduct.core.aq import InitParams
from aqueduct.core.pid import Pid
from aqueduct.core.pid import PidController
from aqueduct.core.pid import Schedule
from aqueduct.core.pid import ScheduleConstraints
from aqueduct.core.pid import ScheduleParameters
from aqueduct.devices.balance import Balance
from aqueduct.devices.base.utils import DeviceTypes
from aqueduct.devices.pump.peristaltic import PeristalticPump
# Parse the initialization parameters from the command line
params = InitParams.parse()
# Initialize the Aqueduct instance with the provided parameters
aq = Aqueduct(params.user_id, params.ip_address, params.port)
# Perform system initialization if specified
aq.initialize(params.init)
# Set a delay between sending commands to the pump
aq.set_command_delay(0.05)
# Define names for devices
PUMP_NAME = "PUMP"
BAL_NAME = "BALANCE"
# Clear the existing setup and add Peristaltic Pump and Balance devices
aq.clear_setup()
aq.add_device(DeviceTypes.PERISTALTIC_PUMP, PUMP_NAME, 1)
aq.add_device(DeviceTypes.BALANCE, BAL_NAME, 1)
# Retrieve the setup to confirm the added devices
aq.get_setup()
# Retrieve PeristalticPump and Balance instances
pp: PeristalticPump = aq.devices.get(PUMP_NAME)
bal: Balance = aq.devices.get(BAL_NAME)
# Create a start command for the Peristaltic Pump
c = pp.make_start_command(
mode=pp.MODE.Continuous,
direction=pp.STATUS.Clockwise,
rate_value=1,
rate_units=pp.RATE_UNITS.MlMin,
)
commands = pp.make_commands()
pp.set_command(commands, 0, c)
pp.start(commands=commands)
# Get process and control values for PID
process = bal.to_pid_process_value(index=0)
control = pp.to_pid_control_output(index=0)
# Create a PID controller
params = ScheduleParameters()
params.kp = 10.0
params.kd = 5.0
constraints = ScheduleConstraints()
sched = Schedule(params, constraints)
pid = Pid(20)
pid.output_limits = (0, 100)
pid.add_schedule(sched)
pid.enabled = True
pid = PidController("fill_controller", process, control, pid)
# Set noise level for simulation
bal.set_sim_noise(
[
0,
]
)
# Wait for some time
time.sleep(1)
# Create PID controller on Aqueduct
aq.create_pid_controller(pid)
# Perform PID control loop for a duration
start = time.monotonic_ns()
while time.monotonic_ns() < start + 30 * 1e9:
bal.set_sim_rates_of_change(
[
pp.get_ml_min()[0] / 60,
]
)
time.sleep(0.01)
# Change PID parameters and setpoint
pid.pid.schedule[0].change_parameters(kp=30, kd=10)
pid.change_setpoint(40)
# Perform PID control loop again for a duration
start = time.monotonic_ns()
while time.monotonic_ns() < start + 30 * 1e9:
bal.set_sim_rates_of_change(
[
pp.get_ml_min()[0] / 60,
]
)
time.sleep(0.01)
# Delete the created PID controller
pid.delete()